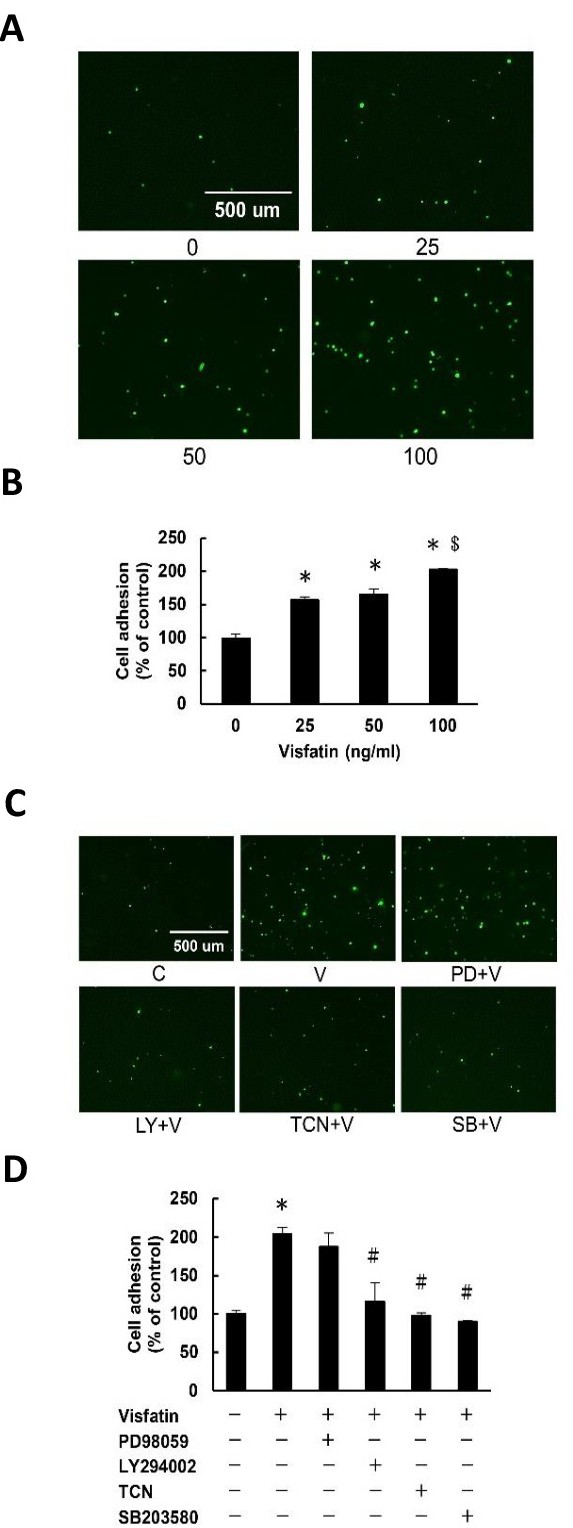
Fig. 1. Visfatin stimulates monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells through the PI3K/Akt- and p38-dependent pathways. (A and B) Cells were incubated with various concentrations of visfatin (0-100 ng/ml) for 24 h, then the adhesion of THP-1 monocytes was measured. (C and D) Cells were pre-incubated for 1 h in the presence of the ERK1/2 inhibitor PD98059 (PD, 30 μM), PI3K inhibitor LY294002 (LY, 30 μM), Akt inhibitor triciribine (TCN, 5 μM), or p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 (SB, 20 μM), followed by incubation in the absence or presence of visfatin (100 ng/ml) in the continued absence or presence of the inhibitor for a further 24 h. Subsequently, the adhesion of THP-1 monocytes was measured. The results are the mean ▒ SEM for three separate experiments, each in triplicate. *P<0.05 compared with the zero control (B) or the untreated control (D); #P<0.05 compared with the visfatin alone group; $P<0.05 compared with the 50 ng/ml visfatin-treated group.